Unlikely State Becomes America’s Surprising New Cancer Epicenter – As Experts Dig into Five Factors Causing a ‘Public Health Crisis’
Researchers studying a sharp rise in cancer cases in Iowa have delved into some of the factors that have made the state America’s unlikely epicenter of new cases.
The state has the fastest growing number of new cancers and the second highest cancer rate in the country for the second year in a row.
This trend left many Midwesterners and officials baffled, as neighboring states, with similar demographics and agricultural practices, actually saw a decline in cancer rates.
But now officials point to a unique environmental cause for the upturn.
It may be related, at least in part, to a geographic anomaly: a radioactive gas seeping out of the Earth thanks to geological changes that occurred during the last ice age.
Each year, the Iowa Cancer Registry and the University of Iowa release a report on how the state’s cancer rates compare to the rest of the country.

Pesticide use is one of five factors likely contributing to the increase in cancer cases in Iowa, officials say.
Radon, a naturally occurring gas released from weathered rock, is the leading cause of lung cancer in non-smokers, according to researchers. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Thousands of years ago, Iowa and other parts of the Midwest were covered by a giant glacier that began to erode the bedrock. Today it is so worn in places that it can leak into the ground and end up in people’s homes.
Experts have now identified five potential factors why lung, breast, prostate and skin cancer rates are rapidly increasing in the Hawkeye State: obesity, radon exposure, tobacco habits, agricultural practices and alcohol consumption.
The interplay of these five factors is likely responsible for this cancer crisis, Mary Charlton, director of the Iowa Cancer Registry and professor at the University of Iowa College of Public Health Department of Epidemiology told the Telegraph Herald.
“The unfortunate, unsatisfactory answer I have for everyone is: It’s not one thing,” Dr. Charlton said. ‘That can’t be the case. We have so many different types of cancer, and they all have different patterns, different geographic patterns, different populations.”
Two in five Iowans are estimated to be diagnosed with cancer 2024 Iowa Cancer Report. That is about 21,000 new cases, of which 6,100 people are expected to die.
The state currently exceeds the national average for the rate of new cancer diagnoses – with about 480 new cases per 100,000 people, compared to the national average of 442 per 100,000.
In recent years, people have learned how environmental factors, such as pesticide use, can increase the risk of cancer, especially in rural areas.
It’s likely, experts say, that pesticide and fertilizer use plays a role in Iowa’s cancer rates. After all, the state uses more agricultural chemicals than any other state, producing 237 million pounds of herbicide and 11.6 billion pounds of fertilizer annually.
When these chemicals enter the water supply, they can build up in the human body and have been linked to cancers of the immune system, brain, breast, bladder, bile ducts of the liver and ovaries.
But other environmental factors, such as radon, can be just as important, the Telegraph Herald reported.
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that is created when rocks and soil are worn away.
When giant glaciers covered the entire Midwest during the last ice age, they began to grate on the rocks and other surfaces that covered this large, flat area.
Those same rocks were so worn that they are now releasing small amounts of gas into the soils of the Midwest, especially in Iowa.
Radon can enter your home from the soil The Iowa Department of Health and Human Services issued a warning. It can sneak through small holes for wiring, plumbing pipes or cracks in a building’s foundation, where it builds up unnoticed unless the room is equipped with radon testing kits.
When someone inhales high levels of radon gas, it damages the lining of their lungs, leading to mutations that can eventually develop into cancer. This is reported by the National Cancer Institute.
According to the EPA, approximately 70 percent of Iowa homes are at risk of radon exposure.
Radon is the leading cause of lung cancer among nonsmokers, the EPA reports. Another factor Iowan officials are taking note of is obesity.
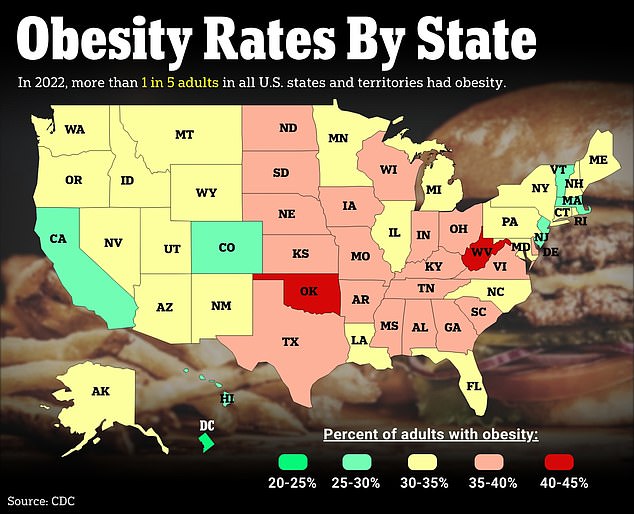
Obesity has been linked to several types of cancer. In Iowa, an average obesity rate and other factors, such as alcohol consumption and radon exposure, are increasing the state’s overall cancer rate.
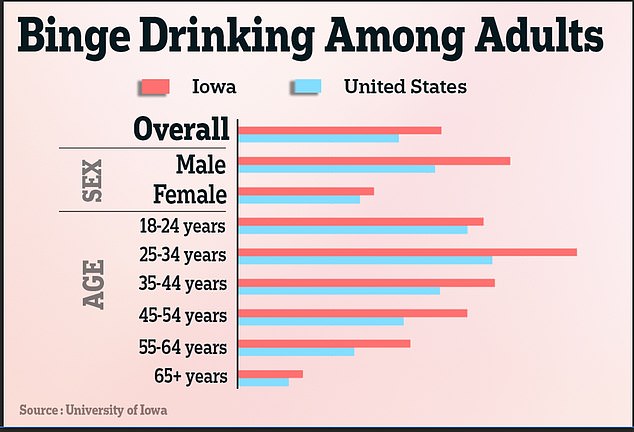
One of the risk factors that officials believe may contribute to cancer cases in Iowa is the drinking habits of the average Iowan.
About 37 percent of Iowan adults are obese. That compares with national averages — where 41.9 percent of adult Americans were obese in 2023, according to the Trust American health.
The incidence of obesity could increase Iowans’ overall risk, putting them in the high-rate category.
Obesity has been identified as a risk factor for cancers of the liver, kidney, stomach, breast, throat, thyroid and ovarian, among others, according to the National Cancer Institute.
‘Overweight and obesity represent a public health crisis and any cancer prevention strategy must include effective weight loss strategies’ Dr. Andrew Nish, said an interventional radiologist and director of the John Stoddard Cancer Center in Iowa.
Most studies that have uncovered this link have been observational – meaning scientists cannot definitively prove that obesity causes cancer. But in some forms of the disease the link is strong.
For example, people with severe obesity are seven more likely to develop endometrial cancer, which affects the uterus, than people with a standard BMI.
A number of theories exist for this.
One is that obesity sometimes causes the body to experience frequent inflammation, the NCI reported. Continued inflammation can put stress on the cells in your body, leading to DNA damage, which in turn can lead to cancer.
Another theory is that fatty tissue produces estrogen. Too much estrogen for an extended period of time has been linked to a number of cancers, the NCI reported.
Officials also emphasized the need to stay away from known risk factors, such as alcohol and tobacco.
Dr. Charlton noted that while smoking habits are trending downward in Iowa, the state is slower to throw away cigarettes than the rest of the country.
In 2021, 14 percent of Midwesterners reported smoking, compared to 11.5 percent of all Americans, the Telegraph Herald reported.
Drinkers are five times more likely to develop throat or mouth cancer than non-drinkers According to the 2024 Cancer in Iowa report. liver, throat, colorectal, oral lip and breast cancer.
About 22 percent of Iowans binge drink, compared to 17 percent of Americans nationwide.
“Compared to other states, more Iowans are drinking, and in greater quantities. This may be why Iowa has the fifth-highest incidence of alcohol-related cancers in the U.S., and the highest rate in the Midwest,” according to the 2024 Cancer in Iowa report.
Considering these five factors may help explain why new cancers are on the rise in different parts of the state, Mary Rose Corrigan, public health director for the city of Dubuque, Iowa, told the Telegraph Herald.
“There are a lot of things that add up to that, and it comes down to lifestyle, access, our environment and policies that help people have healthy lifestyles,” Ms Corrigan said.
