The true face of the ‘Screaming Mummy’ has been revealed: Scientists reconstruct the profile of an Egyptian woman who died screaming in pain 3,500 years ago – before her body was embalmed with her mouth still wide open
The true face of an ancient Egyptian mummy who died screaming in agony has been seen for the first time in 3,500 years after scientists reconstructed her likeness.
The mummy, known as the Screaming Woman, was found in 1935 in Deir Elbahari, Egypt, in the family tomb of the royal architect Senmut.
It is unusual for a mummy to have her organs left inside her. For a long time it was thought that her mouth had been left open by careless embalmers.
But after a recent study revealed that her distorted facial expression was due to a painful death, scientists decided to reconstruct her living face.
Cicero Moraes, the Brazilian graphics expert in charge of the reconstruction, said the end result was a “pleasant sight” created by combining different approaches.

The true face of an ancient Egyptian mummy who died screaming in pain has been seen for the first time in 3,500 years after scientists reconstructed her likeness
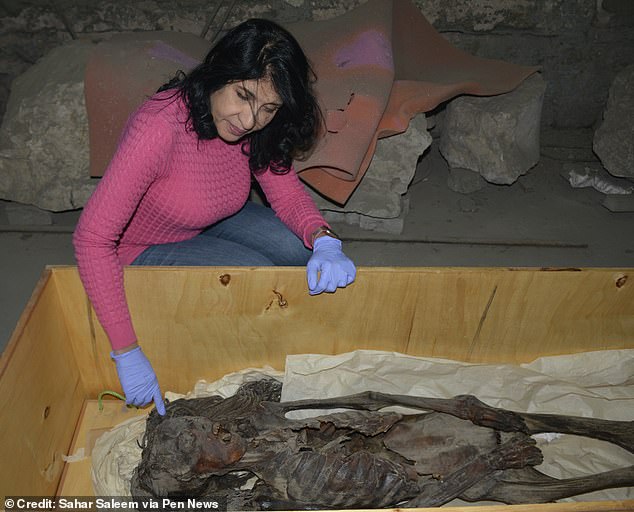

The mummy was found in 1935 in Deir Elbahari, Egypt, in the family tomb of the royal architect Senmut
He said: ‘I used a technique that combines elements from traditional facial reconstruction schools with new approaches based on CT scan data from living people.
‘These projections allow us to discover the spatial boundaries of structures such as the ear, eyes, nose, mouth and the like.
‘In addition, some structures are also drawn in profile, such as the nose and the side surface.
‘The data is supplemented with the anatomical deformation technique, in which the head of a virtual digital donor is adapted to the skull that is to be approximated.
‘In general there is compatibility between all the data, with minor differences, so that the final face is an interpolation of all the information.’
Mr. Moraes created several versions of the face.
The first is objective, with eyes closed and in grayscale, so that no judgment is made about skin color or eye color.
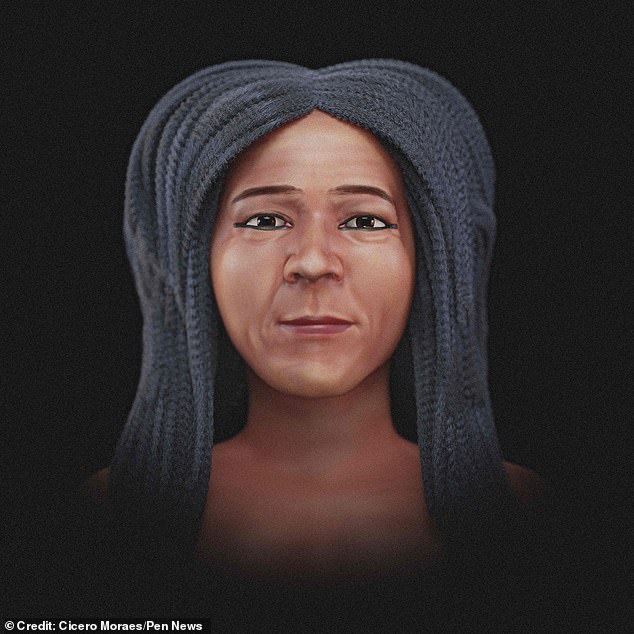
Another is more subjective, showing the woman as she might have looked in real life, in color and wearing the wig she was buried in.
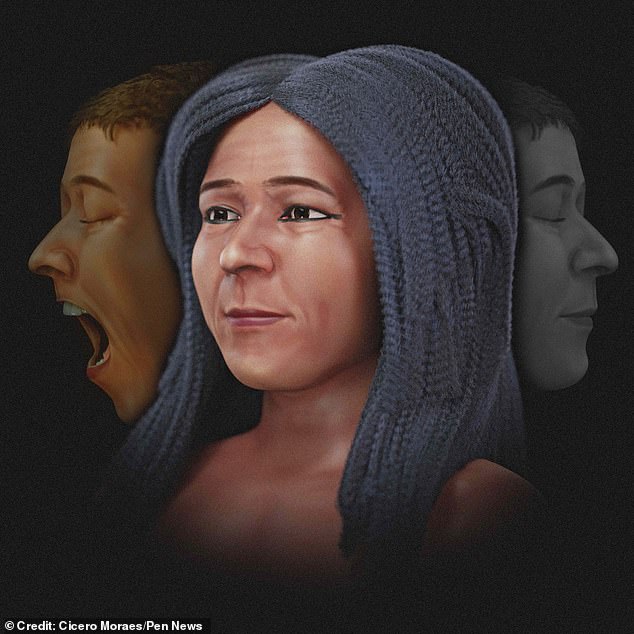

Mr. Moraes created several versions of the face. One is objective, with eyes closed, and in shades of gray to avoid making judgments about skin or eye color (right). Another is more subjective, showing the woman as she might have looked in real life, in color, with the wig she was buried in (center). And a third captures her scream, showing how she would have looked when she was first buried (left).

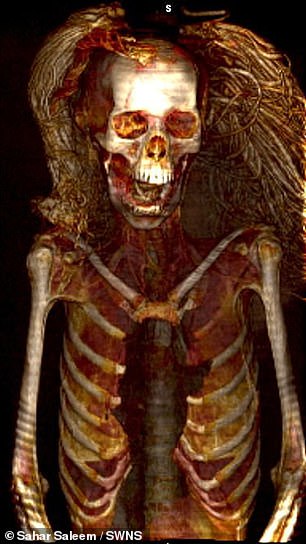
CT images estimate she was approximately 48 years old at the time of her death and that she suffered from mild arthritis of the spine
And on a third, her scream can be seen, showing what she must have looked like when she was first buried.
Mr Moraes knows that his choice of skin colour in the latest images could cause controversy.
He said: ‘The issue of skin colour in ancient Egypt is a source of much controversy, with the discussion shifting from the scientific to the cultural and political.
‘To avoid these problems, I looked for an approach based on publications on the subject, data collected from studies of local groups and ancient Egyptian art.’
Sahar Saleem of Cairo University, lead author of the recent Screaming Woman study, suggested that a corpse spasm was the cause of the mummy’s pained expression.
“She was embalmed with expensive, imported embalming materials,” Dr. Saleem said.
‘This, and the fact that the mummy is so well preserved, contradicts the traditional view that the failure to remove her internal organs indicates poor mummification.’
She continued: ‘The screaming facial expression of the mummy in this study can be interpreted as a spasm of a corpse, implying that the woman died screaming in pain.

Cicero Moraes, the Brazilian graphics expert behind the reconstruction, said the end result was a “pleasant sight” created by combining different approaches
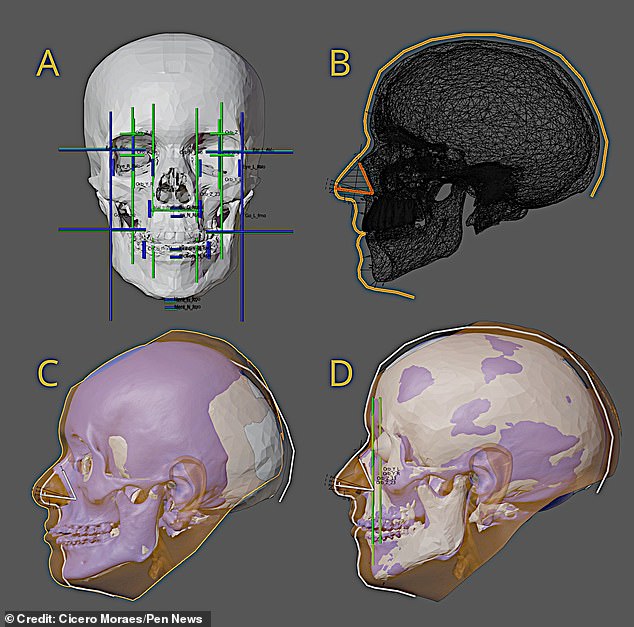
Mr Moraes said: ‘I have used a technique that combines elements from traditional schools of facial reconstruction with new approaches based on CT scan data from living people’
‘This mummified Screaming Woman is a true ‘time capsule’ of how she died, and reveals some of the secrets of mummification.’
However, the cause of her painful death has been lost to history.
Using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy on the remains, Dr. Saleem and her colleagues discovered that the body had been embalmed with juniper and frankincense.
These were expensive. The former was imported from the eastern Mediterranean, the latter from East Africa or South Arabia.
The mummy also wore a wig made from date palm fibers treated with quartz, magnetite and albite crystals.
This was probably to stiffen the locks and dye them black, a color seen as a symbol of youth by ancient Egyptians, Dr. Saleem said.
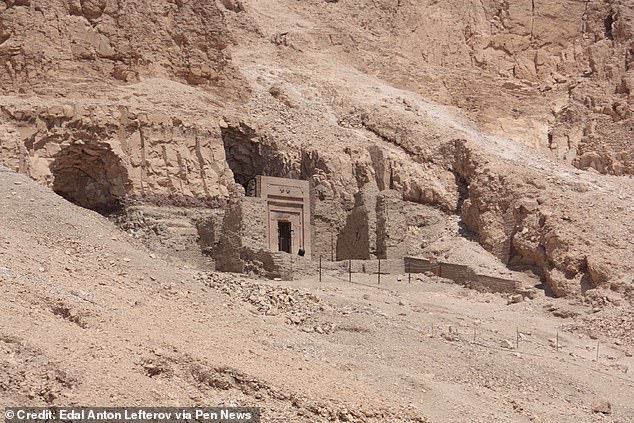

Her remains were discovered in the tomb of Senmut in Deir Elbahari, next to the remains of her parents.


The woman’s coffin did not bear her name, but her burial site near the mortuary temple of the great female pharaoh Hatshepsut offers a clue
She added: ‘The excavation notes noted that she wore two rings with jasper scarabs, set on gold and silver respectively.
‘The material from which these amulets and jewelry are made indicates the wealth and socio-economic status of the person.’
The woman’s coffin does not bear her name, but her tomb at the mortuary temple of the great female pharaoh Hatshepsut does provide a clue.
She was buried next to the parents of Senmut, overseer of the royal works and architect of the temple, who is said to have been the pharaoh’s lover.
“She was likely a close relative of Senmut, who shared his parents’ eternal resting place,” Dr. Saleem said.
Mr Moraes praised Dr Saleem and her co-author, Samia El-Merghani of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities, for their “inspiring” work.
He said, “I really enjoy two things: reading scientific papers and writing them.
‘I had the opportunity to read the article published by Saleem & El-Merghani, who provided the detailed data of the discovery, under a Creative Commons license.
‘I decided to do my bit by putting a face to the discovery.’
Mr. Moraes published his research in the journal OrtogOnLineMag.
