The 40 simple lifestyle tips to keep your brain healthy, according to experts
>
If you ever need an excuse to bust out your bad dance moves, look no further.
For researchers claim it’s just one of 40 simple ways of keeping your brain healthy.
Playing chess, getting off your bus one stop early and reading a book are three other ways of staying sharp in old age.
Scientists say looking after your brain may help reduce the risk of dementia later in life.
Alzheimer’s Research UK has compiled the list of 40 different ‘small, positive changes that you enjoy and can build upon’ to keep your brain healthy
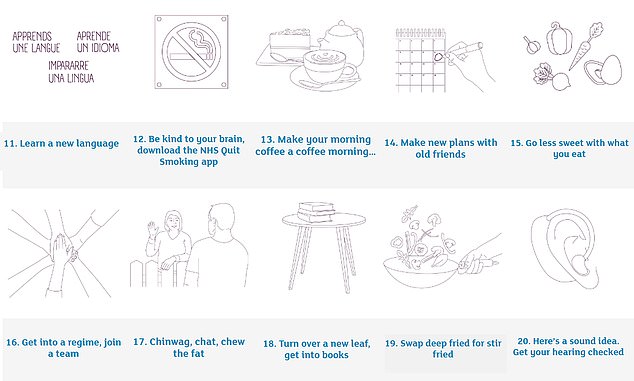
Learning a language, hosting a coffee morning and getting a hearing check are three ways of staying sharp in old age, according to researchers
Alzheimer’s Research UK compiled the list of 40 different ‘small, positive changes that you enjoy and can build upon’.
A survey commissioned by the charity revealed today that just two per cent of Brits are doing everything they can to keep their brains healthy and slash their chances of dementia.
Each lifestyle tweak follows ‘three simple rules’ — loving your heart, staying sharp and keeping connected.
Learning to bake, knit and sew, dig into gardening, taking up a new language and making new plans with old friends are among the 40 measures.
Others are to swap deep fried for stir fried, your cocktail for a mocktail and walk in the park all year round.
Giving up cigarettes was also crucial, experts said, advising people to download the NHS Quit Smoking app.
The team also recommend arranging regular hearing checks, to help drive early detection of dementia, as hearing aids could reduce the progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia.
Data suggests hundreds of thousands of dementia cases could be stopped if people took more steps to prevent it.
Overall, experts say eliminating 12 lifestyle factors would prevent 40 per cent of cases.
These include smoking, hearing impairment, high blood pressure, physical inactivity, excessive alcohol consumption, diabetes, and infrequent social contact.
It has launched an online survey for people to see how they score on the modifiable risk factors, and what they can do now to boost their chances of avoiding it in future.
The Alzheimer’s Society estimates there are more than 900,000 people living with dementia in the UK today. This is projected to rise to 1.6million by 2040.
Dementia itself is an umbrella term used to describe a range of progressive neurological disorders (those affecting the brain) which impact memory, thinking and behaviour.
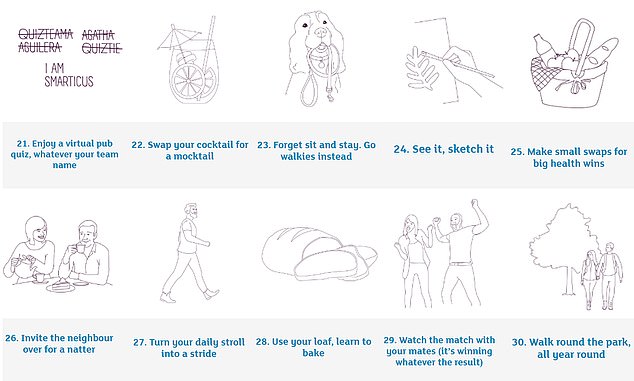
Data suggests hundreds of thousands of dementia cases could be stopped if people took more steps to prevent it. Alzheimer’s Research UK say that overall, eliminating 12 lifestyle factors would prevent 40 per cent of cases

The Alzheimer’s Society also estimates there are more than 900,000 people living with dementia in the UK today. This is projected to rise to 1.6million by 2040
Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia and is estimated to contribute to 60 to 70 per cent of all dementia cases, according to the World Health Organization.
In the US, around 5.5million are thought to be living with Alzheimer’s. A similar rise is expected in the coming years.
Professor Jonathan Schott, chief medical officer for Alzheimer’s Research UK, said the disease had become people’s ‘biggest fear’ over ageing.
He said: ‘Dementia is now the most feared consequence of ageing and so people are wanting to know what they do about their risk.
‘People are coming to us people are going off and getting their genetics done, which of course they can’t change, and then asking about what they can do about modifying risk.
‘The fact that many of the risk factors that were mentioning – blood pressure, smoking and so forth are risk factors for cardiovascular disease and cancer, we can harness this as part of the public health message.’
According to a YouGov survey released today and commissioned by Alzheimer’s Research UK, just one in 50 people are doing everything they can to ward off dementia and look after their brain health
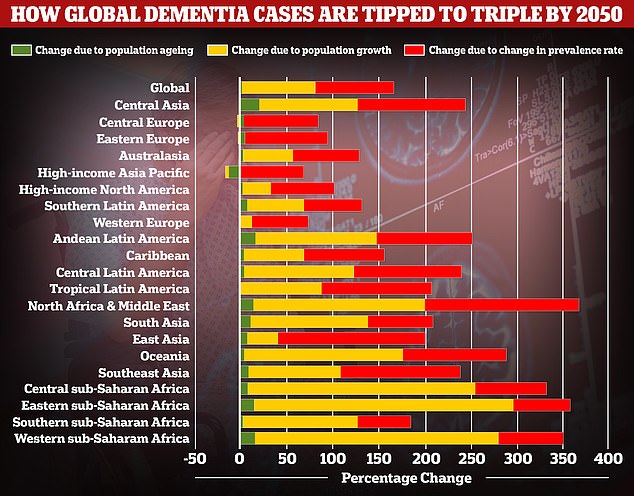
Global dementia cases are set to nearly triple by 2050, from 57.4million to 152.8million, according to a 2021 study by the University of Washington School of Medicine. But the rate the illness is expected to increase varies between different parts of the world. In Western Europe, cases are expected to rise by just 75 per cent, mainly due to an ageing population, while they are expected to double in North America. The biggest increase is expected to be seen in North Africa and the Middle East, where cases are projected to rise by 375 per cent
There is currently no cure for dementia but drugs are available which can slow its progression.
Research has long shown exercise in middle age and beyond can cut the chance of dementia — which is most commonly caused by Alzheimer’s — by up to 40 per cent.
Exercise is thought to help stave off the disease because it improves cognitive function, keeps bodyweight low and prevents plaque forming in the arteries — a key cause of vascular dementia.
Doctors recommend healthy adults get at least 150 of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity a week.
An array of studies have also linked keeping up reading, writing and playing games with delaying the cruel condition’s onset by up to five years, simply by keeping the brain healthy.