Quadrantid Meteor Shower will peak TONIGHT with up to 110 shooting stars every hour – here’s the best time to see it from the UK
- The first meteor shower of 2024 will peak tonight, and you don't want to miss it
- It is among the strongest and most consistent meteor showers throughout the year
<!–
<!–
<!– <!–
<!–
<!–
<!–
If you are a fan of sky watching, make sure you keep an eye on the sky this evening.
The first meteor shower of 2024 will peak tonight, and you don't want to miss it.
The Quadrantid meteor shower lasts from December 28 to January 12, but will reach its highest levels this evening.
Among the strongest and most persistent meteor showers of the year, the Quadrantids can produce up to 110 meteors every hour.
Here's everything you need to know, including how and when to watch the show from the UK.
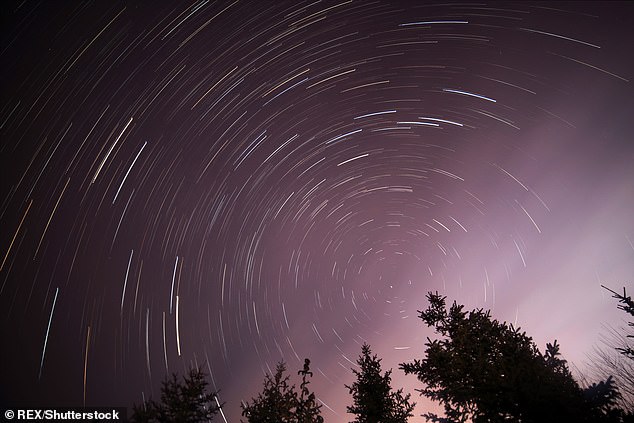

If you are a fan of sky watching, make sure you keep an eye on the sky this evening. The first meteor shower of 2024 will peak tonight, and you don't want to miss it
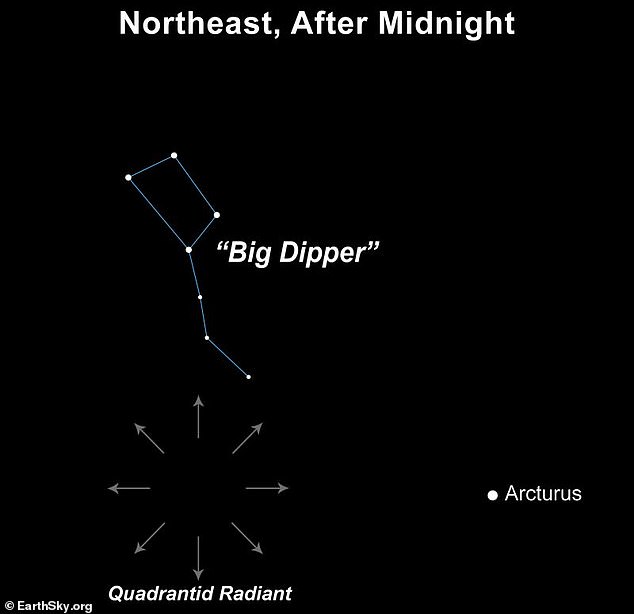

While the meteors appear to radiate from Bootes, the constellation close to the Big Dipper, they actually get their name from the earlier constellation Quadrans Muralis.
Meteorites are pieces of comet and asteroid debris that enter Earth's atmosphere at incredible speeds of up to 43 miles per second.
As they enter, they instantly evaporate, causing streaks of light to appear in the night sky.
The original body of the tetrads remains unclear, although there are two main theories.
Some experts suggest that the meteorites come from an asteroid called 2003 EH1, while others claim that comet 96P/Machholz is responsible.
While the meteors appear to radiate from Bootes, the constellation close to the Big Dipper, they actually get their name from the earlier constellation Quadrans Muralis.
“Quadrans Muralis is now part of Boötes,” Royal Museums Greenwich explained.
Most meteor showers tend to stay at their peak for about two days, but you'll need to be quick to catch the Quadrantids.
The peak will only last about six hours, from late night until dawn tomorrow morning.
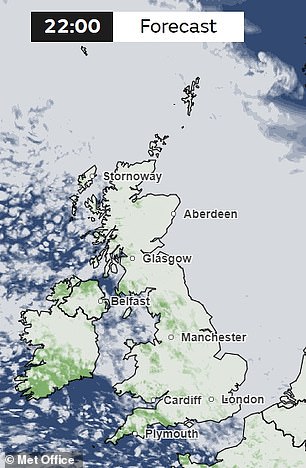

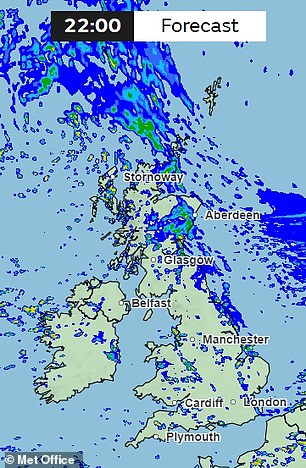

The Met Office is forecasting that tonight will be cold in most parts of the UK, so make sure you keep warm if you venture outside.
For the best viewing conditions, head to a wide open area with little light pollution, around midnight.
Royal Museums Greenwich said: 'Meteor hunting, like the rest of astronomy, is a waiting game, so it's best to bring a comfortable chair to sit in and enjoy the warmth as you can stay outside for a while.'
“They can be seen with the naked eye, so there's no need for binoculars or a telescope, although you will need to allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness for at least 15 minutes beforehand.”
Unfortunately, the peak will coincide with the last quarter moon phase this year, so the moonlight will cause some interference in seeing the meteors.
What's more, the Met Office is forecasting that tonight will be cold across most of the UK, so make sure you stay warm if you venture outside.
The Met Office said: “Some rain has continued in eastern Scotland.”
“Otherwise, it will be a mostly dry night with light winds and some clear spells, and the odd shower in the west. Cool with local frost.
(Tags for translation) Daily Mail
