New CDC data shows record 40% of adults are obese in these three states… so how fat is YOURS?
More states are fatter than ever, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
In 2022, a record three states had more than 40 percent of their adults classified as obese — West Virginia, Louisiana and Oklahoma — and 19 states had a rate above 35 percent.
Thirty states saw their obesity rates rise last year compared to the same period the year before, including the president’s home state of Delaware, where rates rose 11 percent, and New York, where they rose nearly four percent.
By comparison, two states – West Virginia and Kentucky – had an obesity rate over 40 percent in 2021, while in 2012 – just a decade ago – no state had an obesity rate over 35 percent.
The figures prompted CDC experts to say that tackling obesity was an “urgent priority,” describing it as a “disease” linked to “many factors, including eating patterns, physical activity levels and sleep routines.”
The map above shows the obesity rate by US state in the year 2022, the most recent data available. The data was revealed Thursday by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
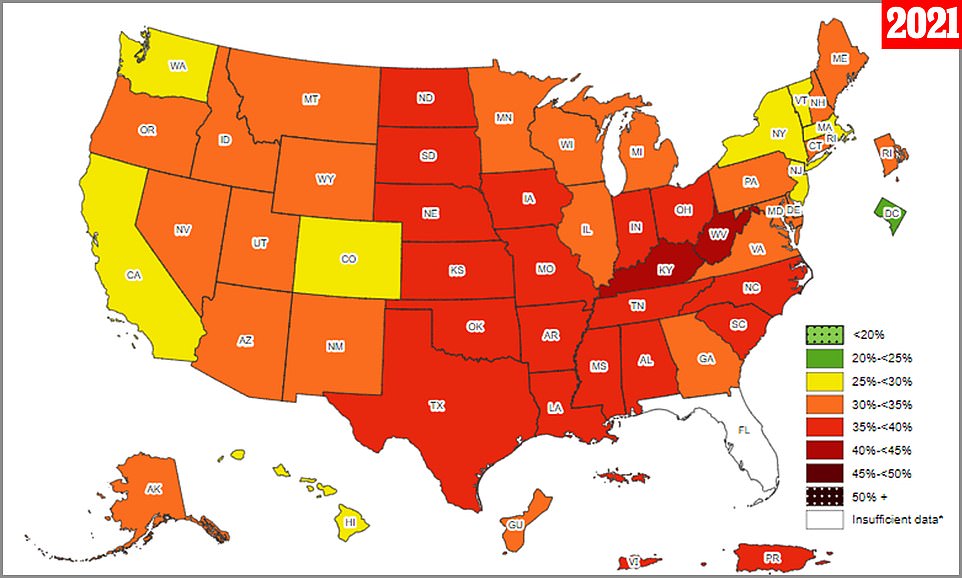
The above data shows the situation of the previous year. A majority of US states saw their obesity rates increase compared to previous years
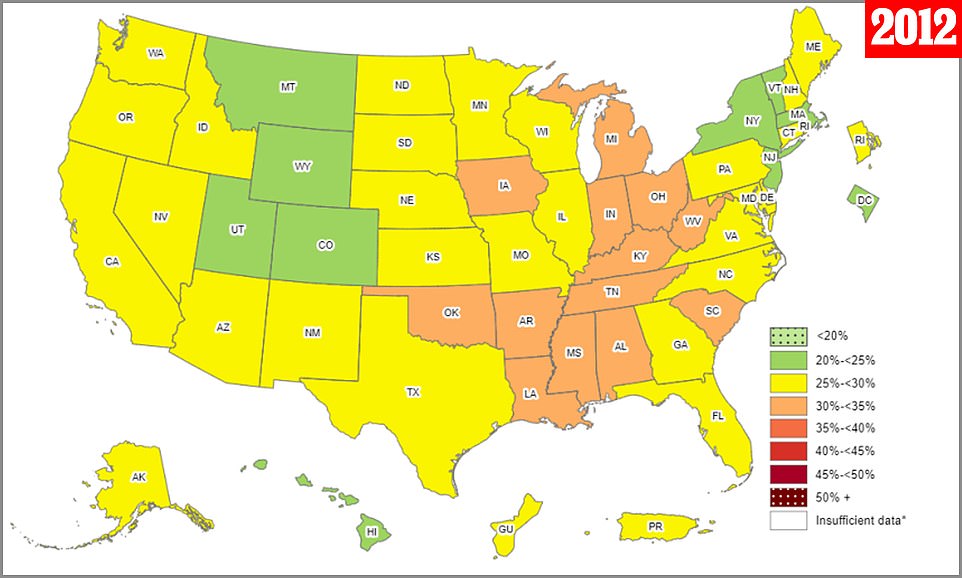
The U.S. obesity rate is up compared to a decade ago, when no state had an obesity rate above 35 percent. The CDC says it is an “urgent priority” to address the nation’s growing waistline
The CDC data was based on the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, which surveys a nationally representative group of 400,000 adults annually to track the nation’s health.
To check waist size, the survey calculates participants’ body mass index (BMI) after asking all participants about their weight and height. This data is then used to estimate the obesity rate by state.
Rounding out the top five states with the highest obesity rates were Mississippi, 39.5 percent, and Tennessee, 38.9 percent.
No state had an obesity rate less than 25 percent, although at the other end of the scale were Colorado 25 percent, Hawaii 25.9 percent, Vermont 26.8 percent and Massachusetts 22.9 percent.
Dr. Karen Hacker, director of the CDC’s Center for Chronic Disease Prevention, said: ‘Our updated maps send a clear message that additional support for the prevention and treatment of obesity is an urgent priority.
‘Obesity is a disease caused by many factors, including eating patterns, physical activity levels, sleep routines, genetics and certain medications. This means that there is no one size fits all approach.
‘However, we know that the key strategies that work include addressing the underlying social determinants of health, such as access to healthcare, healthy and affordable food and safe places for physical activity.’
Data showed that obesity rates in every state were up compared to just a decade ago.
By ethnic group, data showed that black and Hispanic adults were most likely to fall into the obesity category by state.
Previous data has shown that men are also more likely to be obese than women.
Adults are considered obese if they have a BMI of 30 or higher.
For comparison, a healthy BMI – calculated by dividing weight by height, and the answer by height – is between 18.5 and 24.9.
The measure is flawed because muscular people, such as athletes, are often also classified as overweight, but health officials say it’s the best they can do to monitor the situation.
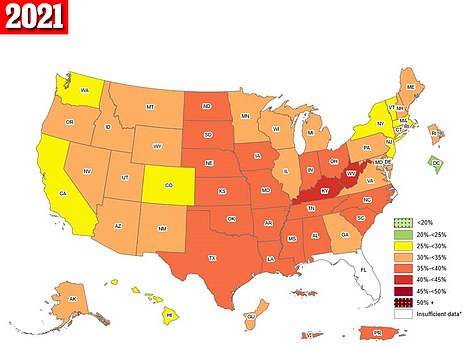
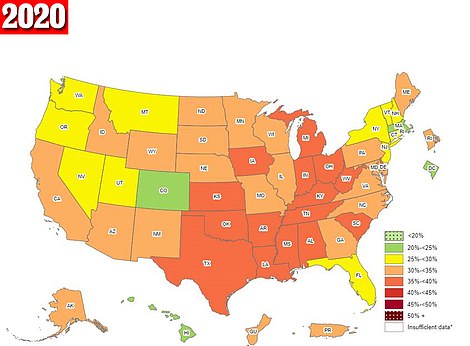
The maps above are the obesity rates across America for the years 2021 (left) and 2020 (right). It showed that Kentucky and West Virginia had the highest rates in the United States
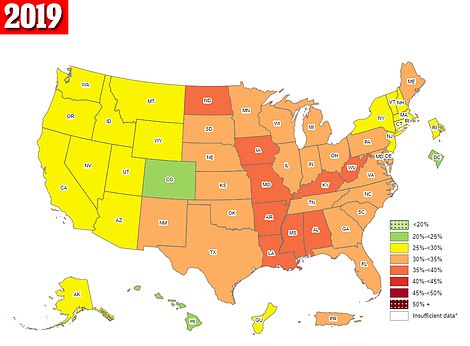
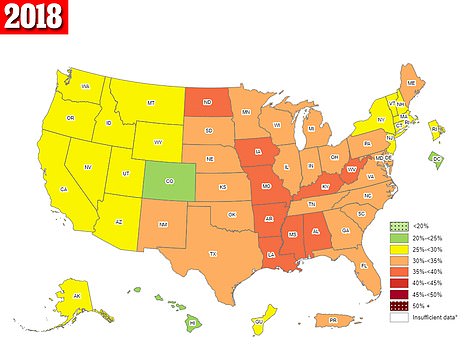
The maps above are for 2019 (left) and 2018 (right). It shows the prevalence of obesity in the US during these two years
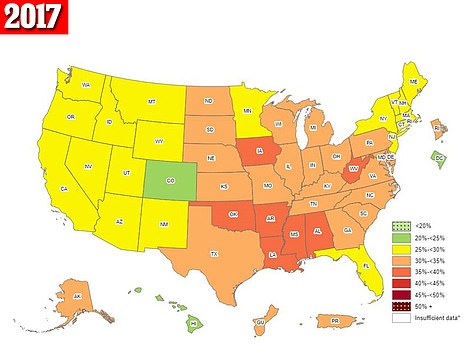
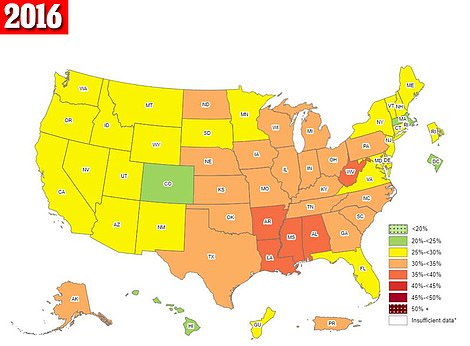
The above maps are self-reported obesity rates in 2017 (left) and 2016 (right). They show that Oklahoma and Iowa saw their rates rise to their highest levels in 2017
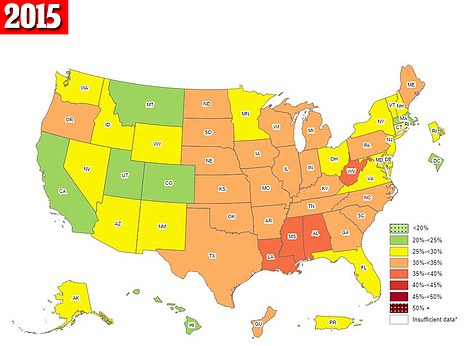
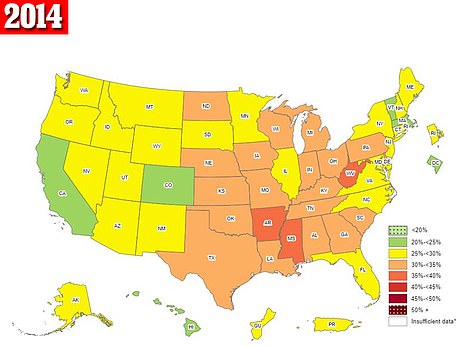
The above shows obesity rates by state for 2015 (left) and 2014 (right). Alabama and Louisiana saw their rates rise to the highest categories during this period
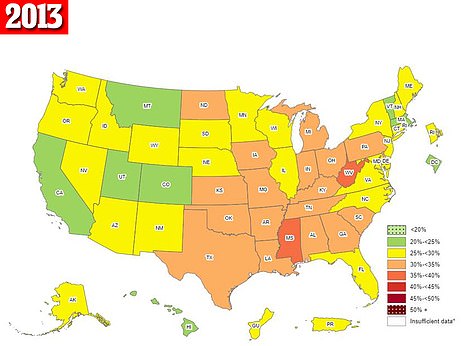
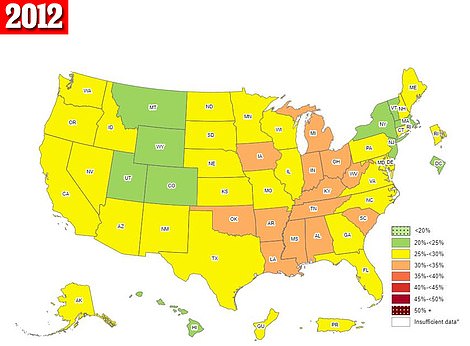
The maps above are for the years 2013 (left) and 2012 (right). They show that both Mississippi and West Virginia saw their obesity rates rise to the highest in the country during this period
Obesity increases the risk of a host of physical conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure and kidney disease.
It is estimated to cost the US healthcare system more than $173 billion annually, while heart disease is the leading cause of death in the US, causing more than 647,000 deaths each year.
There is also evidence that obesity is linked to a higher risk of stroke, serious respiratory infections and twelve different types of cancer.
People with obesity also describe having poor mental health and in some cases being stigmatized because of their weight.
