Fake food made by AI looks tastier than real dishes, scientists say. Can you tell which of these meals are real meals?
Some ultra-processed foods are packed with artificial colors and flavors.
But scientists have discovered that food that is 100 percent artificial looks even tastier than the real thing.
Researchers from the University of Oxford and the University of Naples Federico II discovered that people find AI-generated food images more appetizing.
And as AI images become more realistic, experts warn they could even promote unhealthy eating habits.
Can you separate the real photos from their AI copies? Check your answers at the bottom of the article to see how well you did.

One of these images was generated using OpenAI’s DALL-E 3 – but which one could it be?


The researchers arranged the images according to the basic food type and showed them in three processing stages. For example: a raw carrot, carrot juice and a carrot cake


Experts say the AI-generated versions can use details such as symmetry, color and shape to produce more attractive designs
The researchers showed 297 participants a series of images that were either real photos of food or AI-generated copies.
The AI images were created by putting the original photos into OpenAI’s DALL-E 3 and asking the AI to ‘replicate this photo’.
When the researchers showed the images side by side, the researchers found that the participants were generally very good at spotting what was created by AI and what was real.
The success rate ranged from 62 percent for the carrot juice image to 91 percent for chocolate-covered peanut images.
However, when participants were shown the images individually, they found the task much more difficult.


When the basic ingredient is not eaten raw, the researchers used a photo in which it was simply cooked, as here with these boiled potatoes


The researchers found that people are generally very good at recognizing AI images when they are next to photos


According to the scientists, AI images tend to make food appear more caloric
For images presented individually, the percentage of correctly identifying whether they were real or not dropped to as low as 26 percent in some cases.
In their article, published in Food quality and preferenceThe researchers note that while the success rate remained high overall, there were some exceptions.
They suggest this could be due to the ‘increased complexity of the task’.


The AI images were generated by asking the AI to recreate the original photo. This means that they have not been modified or built from scratch


The researchers say the AI appears to improve the color and shape of the food it depicts


The scientists say AI-generated food images could be used to promote unhealthy eating habits
The most surprising finding, however, is that people seem to find AI-generated images more attractive, especially if they don’t know they were created by AI.
The researchers asked participants to rate the images on a scale from “Not at all appetizing” to “Extremely appetizing.”
They found that when participants were told which image was AI, they generally rated both images about the same.
But when they weren’t told which image was real, participants found that the AI-generated images were significantly more palatable.
They suggest this could be due to the AI using subtle changes in color, symmetry, shape and even the position of the food.


The study found that these images of apples contained the most convincing AI fakes. Can you tell which is which?


The researchers say that AI-generated food images can lead to unrealistic expectations about food


The position of food affects how attractive we find it, which of these looks best based on its position
Lead author Giovanbattista Califano, from the University of Naples Federico II, said: ‘As humans, we often feel uncomfortable when objects point at us and interpret them as threats, even if they are just food.
“When the AI is tasked with replicating food photos with items pointing at the viewer, such as a bunch of carrots or a piece of cake, the AI often positions the food so that it is not pointing directly at the viewer.”
It could be that the AI makes these kinds of subtle adjustments to the images to make them more visually appealing.


Lighting also makes a significant difference in how appetizing food looks to the viewer


AI image generators can now reproduce even small details, making it difficult to tell the difference
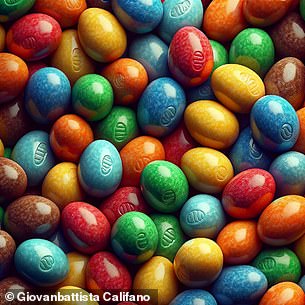
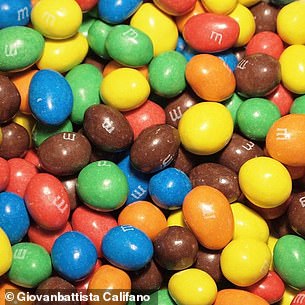
The research found that these two images were the easiest to recognize as real or fake. Can you tell which is which?
However, the researchers also warn that this could lead to problems in the future.
Because using AI to generate images is cheap, fast and easy, study supervisor Professor Charles Spence from the University of Oxford thinks this will become more common.
He said: ‘AI-generated imagery can provide cost-saving opportunities for marketers and the industry by reducing the cost of commissioning food photo shoots.’
Professor Spence also points out that these images pose a risk due to a phenomenon called ‘visual hunger’, where viewing images of food triggers appetite and cravings.
The study found that AI-generated images not only look better than the real thing, but also tend to portray foods as higher in calories.
The AI tended to show more food in each image, for example more chips or larger portions of whipped cream.
If these images spread widely, Professor Spence suggests it could lead to people making less healthy choices about their food.
Professor Spence says: ‘This could potentially influence unhealthy eating behavior or promote unrealistic expectations about food among consumers.’
