Expert reveals what’s causing your cough that won’t go away, and how to get rid of it for good
It may seem like everyone you know is sick: people are calling out of work and friends are canceling plans.
With the recent spikes in flu, Covid and RSV, as part of the US tripledemic, more and more people are struggling with a runny nose or sore throat.
For many, these symptoms are accompanied by a nasty cough that won’t go away.
However, doctors have revealed what a cough actually means and tips on how to get rid of it for good.
Dr. Malathy Munisamy, a clinical research physician at MAC Clinical research in Britain said that while coughing can be annoying, it is a normal defense mechanism.
“Coughing is simply the body’s natural response to any irritation in the airways,” he said.
The US is in the midst of a surge in flu and cold cases. However, a nasty cough can be a sign of several conditions, doctors warn
These can include germs, mucus, and dust, among other pollutants.
Dr. Munisamy said: ‘Standard cough, which is often ‘harmless’, clears up on its own within a few weeks.’
However, those that linger could be a sign of a cold, flu, or a serious infection like pneumonia.
While the average cough after an infection lasts about 18 days, Dr. Munisamy divides coughs into three categories depending on how long they last: acute, subacute and chronic.
An acute cough is a cough that lasts less than three weeks. In many cases, this persistent cough can be due to a common cold, flu, or nasal drip caused by allergies or a virus.
Post-nasal drip is when excess mucus builds up in the back of the throat and drips down. This may cause you to feel a tickle in the back of your throat, swallow frequently, cause hoarseness, nausea, and a constant urge to clear your throat.
It can also lead to chronic cough.
Dr. Munisamy recommends using a steroid-based nasal spray such as Afrin or Flonase to relieve inflammation in the nose and reduce mucus.

The color of your snot can give you a few hints as to why you have a runny nose. In some cases, for example if it is clear, it is relatively harmless and is usually caused by pollen allergies. However, if it is black, it may indicate that you have been infected with a deadly fungus
He said: ‘As this cough is caused by a virus, rest, hydration, paracetamol, ibuprofen or cold medicines are usually effective treatments.’
But avoid antibiotics in these cases: ‘If you use antibiotics against viruses, they will not work and can lead to bacterial antibiotic resistance.’
A cough that lasts three to eight weeks is known as a subacute cough.
Dr. Munisamy said this could be a sign of respiratory infections such as bronchitis, whooping cough or pneumonia.
Bronchitis is an infection of the large airways, also called the bronchi, which travel between the trachea and the smaller airways.
The Mayo Clinic states that the initial illness usually clears up within a week to ten days, but the cough can last for several weeks and antibiotics are usually not recommended.
Whooping cough, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious infection characterized by a severe, hacking cough and treated with a course of antibiotics. Doctors say it is very important to treat whooping cough early, before the coughing starts, because delaying treatment will make the treatment ineffective.
And pneumonia inflames the air sacs of the lungs, causing them to fill with fluid. Some forms of pneumonia can be treated with antibiotics, while others can be prevented by vaccinations.
Along with a cough that can produce phlegm — a type of phlegm that comes from the lungs and throat — symptoms include chest pain when you breathe or cough, confusion, fatigue, fever, chills, low body temperature, nausea, and shortness of breath.

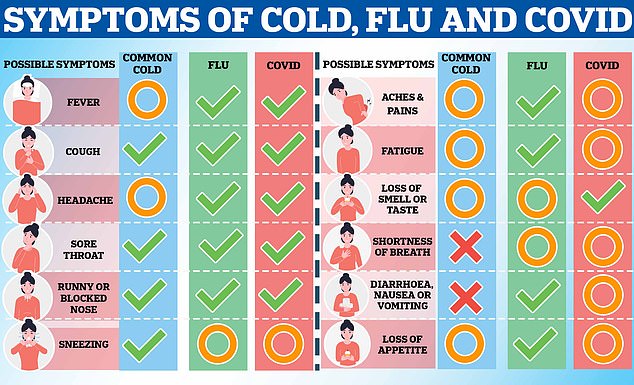
The above shows the common symptoms (green check mark), occasional and possible symptoms (orange circle) and the symptoms that never occur (red cross) for colds, flu and Covid
Dr. Munisamy said: ‘Chest infections can be viral or bacterial, and each requires different treatment.
‘Antiviral medication or an antibiotic may be prescribed in addition to the usual advice of rest, paracetamol and hydration.’
Treating all of these respiratory conditions early can reduce the chance of developing a persistent cough that lasts long after other symptoms have gone away.
The doctor also noted that a subacute cough can also be a sign of Covid-19. He said a characteristic of the Covid cough is one that is new and persistent, meaning the cough lasts for more than an hour or you have three or more coughing fits within 24 hours.
Treatments for Covid include largely the same treatments as those for colds and flu, plus the drug Paxlovid, which can be prescribed by a doctor.
If you have a cough for more than eight weeks, Dr. Munisamy warns that you may be experiencing a chronic cough, which could be a sign of a more serious condition.
One of these is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), an inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow.
According to the Mayo Clinic, this leads to difficulty breathing, as well as wheezing, chest tightness, frequent respiratory infections, lack of energy, unintentional weight loss and swelling in the ankles, feet or legs.
Smoking is the most important risk factor for COPD.
According to the World Health Organization, COPD is the sixth leading cause of death in the world. It affects 16 million Americans.
There is currently no cure for this progressive disease, but there are lifestyle changes that can help alleviate symptoms and aim to extend life expectancy,” Dr Munisamy said.
‘These include smoking cessation, bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation and oxygen therapy.’
He also points to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) as a possible cause of chronic cough, which causes scarring of the lungs.
Although the condition is progressive, Dr. Munisamy recommends the use of supplemental oxygen and, in extreme cases, lung transplantation to reduce symptoms.
A chronic cough can also be a sign of lung cancer, the deadliest form of cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
It is responsible for one in five cancer deaths.
Standard treatments for lung cancer include a combination of chemotherapy, radiation and surgery.
As a general rule of thumb, Dr. Munisamy said if your cough lasts more than three weeks, it’s time to see a doctor.
He added: ‘Any cough accompanied by distressing or serious symptoms such as coughing up blood, hoarseness of voice, shortness of breath, fever, weight loss, difficulty swallowing or vomiting should be assessed by your doctor immediately.’
