Eating a popular fruit may reduce your risk of dementia
- One study found that adults who consumed strawberries reported better cognition
- Strawberries contain antioxidants that reduce inflammation and chronic diseases
- READ MORE: Revealed: The science-backed diet could reduce your risk of dementia
Eating strawberries may reduce the risk of dementia, a study suggests.
Researchers looked at overweight participants who had complained of mild cognitive impairment and asked half to abstain from eating any kind of berry, while a second group ate the equivalent of a cup of strawberries every day.
The results showed that those who consumed the strawberry powder performed better on tests that measured how well they could remember a list of words after 12 weeks.
The study builds on the team’s previous research on blueberries, blackcurrants and other berries shown to reduce the risk of dementia.
This is because blueberries and strawberries contain antioxidants called anthocyanins, which fight unstable molecules known as free radicals that cause chronic inflammation, a risk factor for dementia.
Strawberries are packed with antioxidants called anthocyanins, which fight unstable molecules known as free radicals that contribute to diseases such as inflammation, diabetes and dementia.
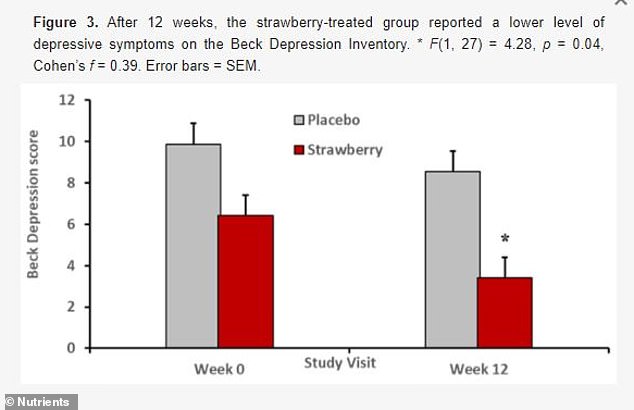
Participants who consumed the strawberry powder reported fewer depressive symptoms
Dr. Robert Krikorian, lead author of the study and professor emeritus at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, said: ‘There is epidemiological data to suggest that people who regularly consume strawberries or blueberries experience a slower rate of cognitive decline as they age. experienced.’
The researchers evaluated 30 overweight patients – five men and 25 women – between the ages of 50 and 65 who complained of mild cognitive impairment. Dr. Krikorian said they chose this group because they have an increased risk of dementia.
For 12 weeks, participants were asked not to consume berries, except for a daily packet of supplement powder mixed with water during breakfast. This was equal to one cup of whole strawberries.
Half of the participants received the powder, while the other half received a placebo.
They were then given memory tests and researchers monitored their mood, the amount of depressive symptoms and their metabolism.
Those who consumed the strawberry powder performed better on memory tests and reported having fewer depressive symptoms.
The study builds on the team’s previous research, which was published in the journal Nutrients and found that blueberries also reduced symptoms of cognitive decline.
Berries are a staple of the MIND diet, a combination of the Mediterranean and DASH diets. This diet prioritizes anti-inflammatory foods such as salmon, lentils, avocados, carrots and cauliflower.
More than 6 million Americans are believed to suffer from dementia This is reported by the Alzheimer’s Association.
By 2050, this is expected to rise to almost 13 million as the older population grows – or one in 25 people.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says early symptoms of the condition include memory loss, problems maintaining attention and communicating with others.
This may include getting lost in a familiar neighborhood, using unusual words to refer to familiar objects, and forgetting the names of family members.
Being older is the biggest risk factor for developing the condition, along with a family history of it and a higher risk of heart disease.
There is currently no cure for dementia, but treatments instead focus on slowing the condition and limiting its symptoms.
The authors said limitations include the small sample size and length of the study.
The research was published in the journal last month Nutrients.
