Chlamydia and syphilis infections fall by 80 percent in the US thanks to ‘Morning after pill for STDs’ – but Brits are still denied treatment
A ‘morning after pill’ could reduce rising rates of sexually transmitted infections (STDs), according to new research.
Those who took the common antibiotic doxycycline within 72 hours of sex reduced their chances of contracting syphilis and chlamydia by as much as 80 percent.
Experts suggested it could be a vital new weapon in the fight against rising STDs, as it is unlikely to have an impact on antimicrobial resistance.
The number of STDs has risen dramatically in the UK and America in recent years, with changing sexual behavior and resistance to treatment believed to be behind the increase.
Rising divorce rates, the rise of erectile dysfunction treatment Viagra, dating apps and the growth of retirement villages have increased infections among middle-aged and older groups.
Concerns have also been raised about children copying what they see in pornography, which they can freely access on their mobile phones.
The trend has led to a call for new strategies to tackle poor sexual health, especially among older generations who may have missed out on safe sex education.
In the first ‘real’ study into the potential of doxycyclines as STD prevention, researchers from the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute in the US gave it to 2,253 people who were already taking preventive HIV medication, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).
Those who took the common antibiotic doxycycline within 72 hours after sex reduced their risk of syphilis and chlamydia by as much as 80 percent
They looked at STD test results before and after taking the pills, known as doxyPEP, to understand how this might have affected the risk of getting STDs.
They found that the incidence for chlamydia fell by 79 percent, for syphilis by 80 percent and for gonorrhea by 12 percent, according to the findings published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Doxycycline costs just a few cents and is given by the NHS to people to treat bacterial conditions such as chest and dental infections, as well as STDs, syphilis and chlamydia once they have an infection.
It is not yet used as a preventative treatment in the UK, despite increasing noise around it as a viable option for reducing STDs.
British sexual health leaders are said to be considering guidelines but are concerned about the possibility that resistant strains of infection could emerge if the antibiotics are used more widely.
According to the UK Health Security Agency, 401,800 new STDs were diagnosed in England last year, an increase of 4.7 percent from 383,789 in 2022.
The strongest year-on-year increase was among children aged 13 and 14, where the number rose by almost a fifth (19.5 percent) to 459.
This was followed by pensioners aged 65 and over, with the number of new cases rising 18.2 per cent to 2,885.
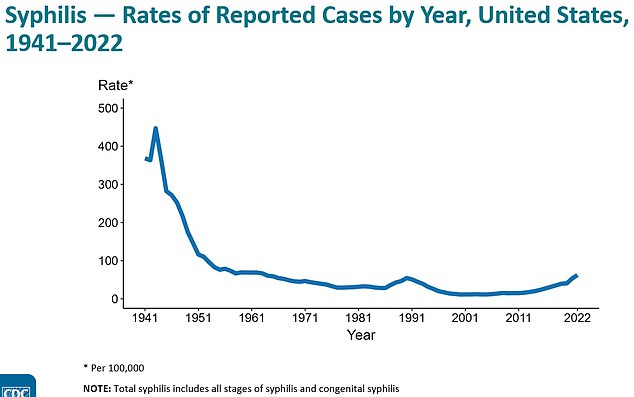
The chart above shows the rate per 100,000 people for the total number of syphilis cases recorded in the US since the 1940s. It shows that they are starting to tick again
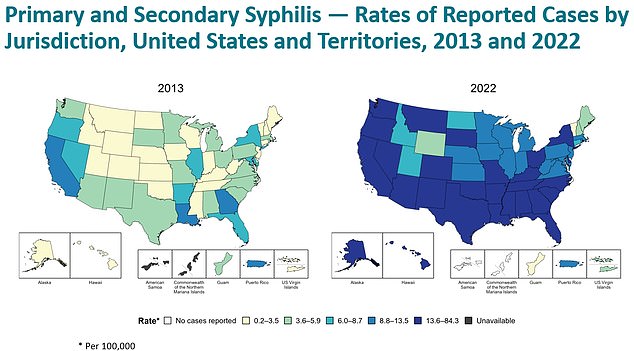
The two maps show how the number of syphilis cases in the US has shifted since 2013
Syphilis cases are at their highest level since 1948, with 9,513 cases reported last year.
Although the majority of cases were in gay men, the UKHSA said there was a greater “proportionate increase” in the number of syphilis diagnoses among heterosexual men and women.
In 2023, 1,958 cases were diagnosed among heterosexual men and women, a 22 percent increase from 2022, when there were 1,608 cases.
Among gay men, the number of cases increased by seven percent between 2022 and 2023.
And a major outbreak of syphilis is gripping the US, with cases reaching their highest level since the 1950s, official data shows.
An annual report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) last year found that 207,300 cases of the STD — which can cause sores on the genitals and mouth — were diagnosed nationwide in 2022, the latest year available.
That represented an increase of 17 percent in one year and an increase of 83 percent compared to five years ago.
The data also shows that cases of congenital syphilis increase by 30 percent – when the mother passes the disease to her baby – which is of particular concern because it poses a risk of stillbirth and birth defects.
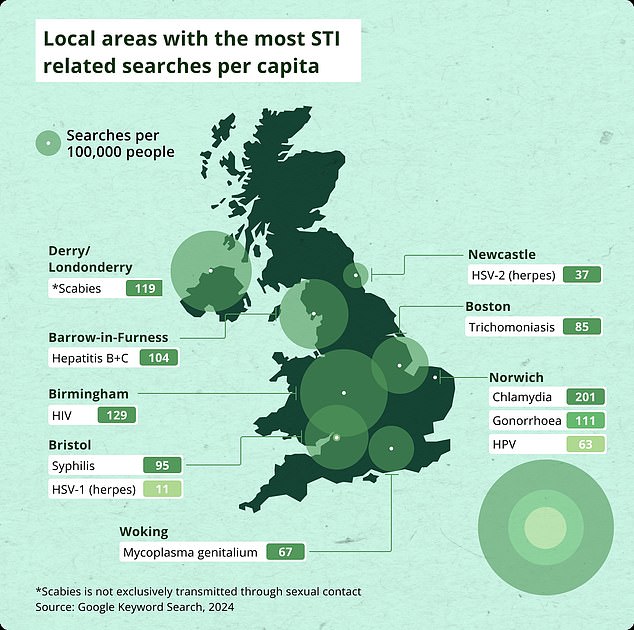
Norwich has been named as the UK hotspot for sexually transmitted infections (STIs), chlamydia, gonorrhea and genital warts, new analysis shows
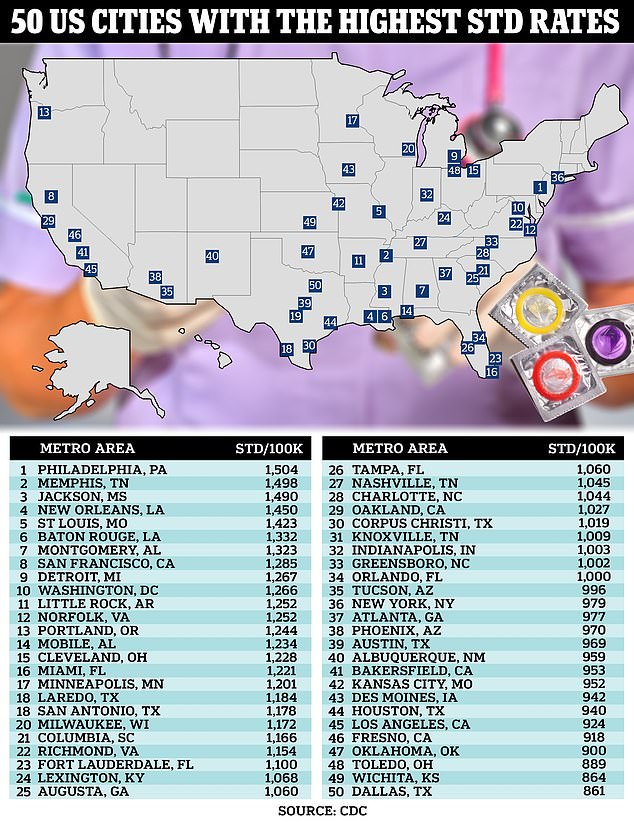
The number of STDs has risen dramatically in Britain and America in recent years, with changing sexual behavior and resistance to treatment believed to be behind the rise.
They looked at STD test results before and after taking doxycycline, also known as doxyPEP, to understand how it might have affected the risk of getting STDs.
Lead author of the new doxyPEP study, Dr. Michael Traeger, said he was “excited” by the findings showing its potential effectiveness outside the clinical setting.
“Interventions that are effective in clinical trials don’t always work in practice, where people tend to face more barriers to consistent medication use,” he said.
Dr. Julia Marcus, senior author of the study, said: ‘We know there are important questions that remain to be answered about doxyPEP, including its effects on antimicrobial resistance.
‘In the meantime, our study suggests that wider implementation of doxyPEP could have enormous benefits for reducing STD transmission and improving sexual health.’
Despite hopes of preventing syphilis and chlamydia, experts in the field of gonorrhea, for example, which can cause pain, discharge and infertility, are almost completely resistant to doxycycline.
There were 85,223 cases of gonorrhea diagnosed last year, the highest number since records began in 1918.
Chlamydia was responsible for almost half of all new STDs discovered in Britain, with 194,970 diagnoses in 2023.
There were also 27,167 first episodes of genital herpes and 26,133 new genital warts.
Despite this, new STD diagnoses remain below pre-pandemic levels, with 468,139 cases recorded in 2019.
