Chinese scientists develop shot that appears to ‘reverse’ autism in mice studies
- Researchers changed a genetic mutation associated with autism in mice
- Mice that received the injection showed fewer signs of the condition
- READ MORE: 13 Giveaway Signs of Autism in Adults Revealed
Chinese scientists are developing an injection that they say could treat autism symptoms.
The injection has only been used in mice so far, but researchers say their evidence suggests it could 'feasibly' be used to help people with the spectrum disorder.
Shanghai scientists injected mice with a gene-editing tool that changed a particular mutation in DNA linked to autism symptoms.
Mice with the genetic trait that received the injection had a complete reversal of their behavioral and social problems.

Autism is typically diagnosed in children, and about one in 36 American children were diagnosed in 2020, according to official figures.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has been linked to a mutation in the MEF2C gene.
The poorly functioning DNA causes problems with crucial developmental processes in the brain.
Although the scientists – from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine and Fudan University in Shanghai – focused on one gene – they caution that it is likely that multiple genetic mutations are involved in the development of autism.
Previous studies have linked more than 200 genetic mutations to ASD, most of which are not hereditary.
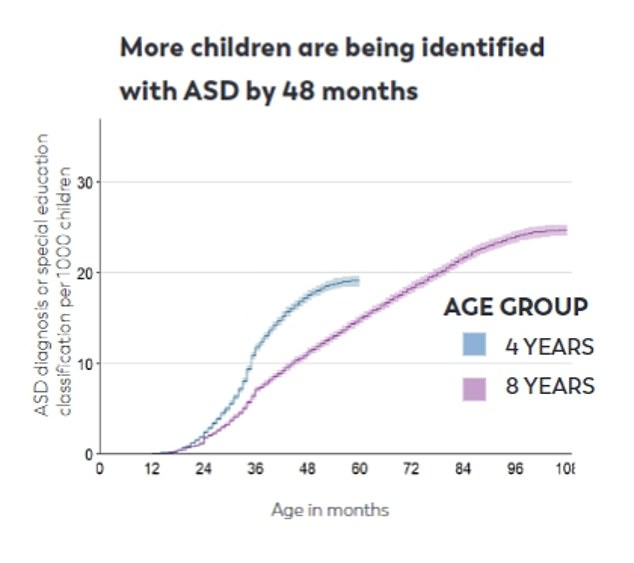
The CDC chart shows progress has been made in the early diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders in the US. This is crucial because the sooner a child is diagnosed, the sooner they can access support
These scientists chose to focus on one gene – called MEF2C – because children with mutations or deletions in it, living in China and Korea, are known to be more likely than others to be diagnosed with the disorder.
The MEF2C gene is strongly involved in neurological development, both in utero and in childhood.
It programs functioning in brain regions integral to learning and memory, such as the frontal cortex and hippocampus.
For the study, published in the journal Nature Neurosciencethe researchers packaged their gene-editing potion in a virus, which was injected into the brains of the mice.
Using a virus, the active ingredient can do that cross the blood-brain barrier, a network of blood vessels and tissue that lines the inside of the brain and protects it from invaders.
The authors said: 'This treatment successfully restored MEF2C protein levels in several brain regions and reversed behavioral abnormalities in MEF2C mutant mice.
Autism is typically diagnosed in children, and in 2020, approximately one in 36 children was diagnosed.
This marked a significant increase from the estimate of 1 in 44 in 2021, and again from 1 in 110 in 2006.
Experts say the increase in cases is not necessarily clear that autism is on the rise, but an increase in awareness means doctors can spot it better.
About 5.4 million American adults – 2.2 percent of the US population – have been diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder.
Autism varies in severity, but typically causes a person to find it difficult to adapt to changes in routine.
Some of those affected also experience cognitive and language problems and may have difficulty interacting and socializing with others.
The disorder exists along a spectrum, meaning there is wide variation in severity and how symptoms present. Some people have mild forms of the condition that require little additional support.
For others, the condition can be a serious, lifelong disability.
About a quarter of children with ASD are minimally verbal, meaning they speak about 30 words.
Autism can sometimes be different in girls and boys, with autistic girls known to hide signs of the disorder by 'masking' them to fit in with others. Boys are about four times as likely to be diagnosed.
Caring for a child with ASD can be very difficult for parents, who often have to make special arrangements for their education and social interactions with other children.
Screenings for ASD are advised at 18 months and 24 months, where the child's language, movement and thinking skills, as well as behavior and emotions, can be compared with the rest of their age group.
