The WORLD’S largest dinosaur skeleton is up for sale: The enormous Apatosaurus named ‘Vulcain’ is 21 metres long and over 80% complete – and could fetch a whopping £4.2MILLION at auction
- Dinosaur fans get the chance to own the largest skeleton in the world
- It is expected to fetch between £2.5 million and £4.2 million at auction
It is the extinct beasts that inspire awe in young and old.
But now, dinosaur superfans have the chance to own the world’s largest skeleton: an Apatosaurus named Vulcain.
This herbivorous species, whose name means “deceptive lizard” in Greek, grew to 70 feet (21 m) long and lived in an area that is now North America.
They are closely related to the famous Brontosaurus and are considered one of the largest land animals of all time.
They had a long, narrow tail that they may have used as a whip against predators, or to maintain balance while walking.
It’s the extinct beasts that inspire awe in young and old alike. But now dinosaur superfans have the chance to own the world’s largest skeleton: an Apatosaurus named Vulcain.


An auction house in Paris will sell the copy on November 16 and it is expected to fetch between £2.5 million and £4.2 million.
The animal was enormous – it weighed as much as five adult elephants – and lived in herds.
The copy will be auctioned at an auction house in Paris on November 16. It is expected to fetch between £2.5 million and £4.2 million.
Anyone who buys the dinosaur will also receive GPS data of the site where it was excavated and the excavation plan.
The skeleton of an adult human is more than 80 percent complete and about 150 million years old.
It was discovered in 2018 in Wyoming, United States. It took three years of excavation.
It will be on display to the public until the auction at the Domaine de Dampierre-en-Yvelines, a chateau, park and gardens 45 minutes outside Paris.
In 2020, an anonymous buyer purchased Stan, a 12-metre-long T-Rex skeleton, for more than £25 million at an auction in New York, making it the most expensive fossil to date.
Paleontologists have previously warned that private collectors’ interest in dinosaur bones is making them unaffordable for museums around the world.
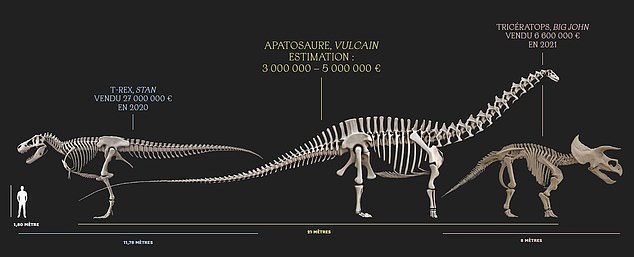
In 2020, an anonymous buyer purchased Stan, a 12-metre-long T-Rex skeleton, for more than £25 million at an auction in New York – making it the most expensive fossil to date
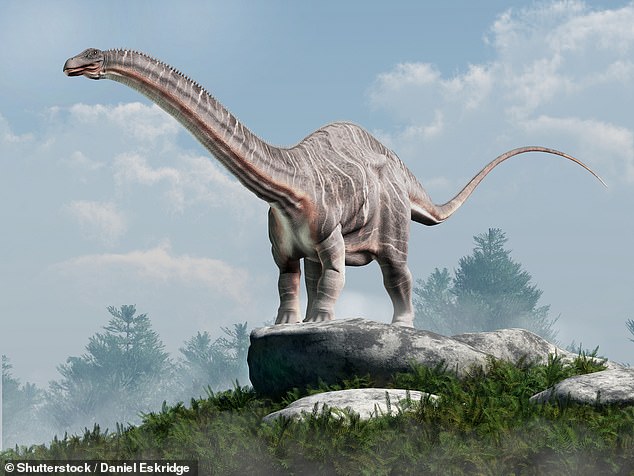

This herbivorous species, whose name means “deceptive lizard” in Greek, grew to 70 feet (21 m) long and lived in an area that is now North America
