Thinstagram! Selfies make you look slimmer than normal photos, study finds
>
- 272 people were asked to rate photos of 10 volunteer models wearing sportswear
- Each model was photographed from several angles, including a selfie at arm’s length
When you open Facebook or Instagram, your feed is likely full of selfies.
Photographs, taken by someone who holds the camera away from their body but pointing it toward themselves, have become increasingly popular in recent years.
But rather than just being a self-indulgence fad, the craze is actually backed by science – because it makes you look thinner, according to experts.
In a new study, participants tended to rate women’s bodies as thinner when viewed in selfies compared to photos taken from other angles.
Researchers from York St John’s University and the University of York asked 272 people to rate photos of 10 volunteer models wearing sportswear.

Common: When you open Facebook or Instagram, your feed is likely full of selfies. But a new study finds that this craze is actually backed by science – because it makes you look thinner, according to experts (stock image)
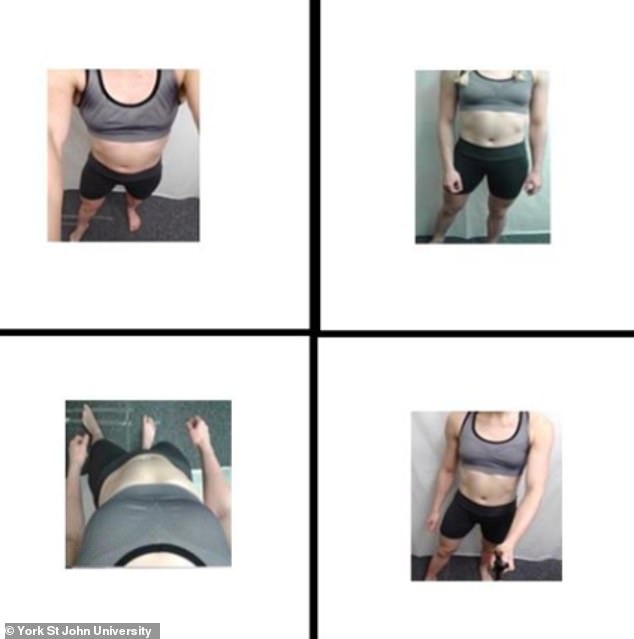
With faces excluded, each model’s body was photographed from several angles – from a traditional external perspective (top right), a portrait taken at arm’s length (top left), a selfie taken with a selfie stick (bottom right) or from a photograph Volunteer. Special perspective (bottom left), where the camera looks down from the chin
With faces excluded, each model’s body was photographed from several angles – from a traditional outside perspective, a selfie taken at arm’s length, a selfie taken with a selfie stick or from the perspective of the volunteer themselves, with the camera pointed down from the chin.
The analysis revealed that participants tended to judge bodies in selfies as thinner than bodies in photos with an external perspective.
Meanwhile, photos taken from the chin down were considered the slimmest and least attractive.
The findings could reflect links between social media use and body dissatisfaction, the researchers said.
“Many of us see selfies every day as we browse the growing number of social media platforms,” they said.
“We know that filters can change the way objects appear.
“This research suggests that the angle from which a photo is taken can change our judgments about body size, so when consuming images online, even simple, unfiltered selfies, what we see is not necessarily an accurate representation of real life.”
Writing in the magazine One plus“Participants may have viewed selfies as more attractive because of the qualities they convey or are associated with them,” they added.
“Selfies have been suggested to endorse the idea that the person in the photo is more extroverted, sociable and open to experience.

Research: Looking at selfies could be ‘more harmful’ than other images on social media for people at risk of developing eating disorders, the team said
“However, selfies have also been linked to more negative personality traits such as narcissism and untrustworthiness.”
The results also revealed that people with a higher level of eating disorder symptoms also evaluated the objects in selfies more positively.
The team said this may suggest that looking at selfies could be “more harmful” than other images on social media for people at risk of developing eating disorders.
(Tags for translation)dailymail
